11.4. Apache HTTP Server Configuration
Caution
Do not edit the /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf configuration file by hand if you wish to use this tool. The HTTP Configuration Tool generates this file after you save your changes and exit the program. If you want to add additional modules or configuration options that are not available in HTTP Configuration Tool, you cannot use this tool.
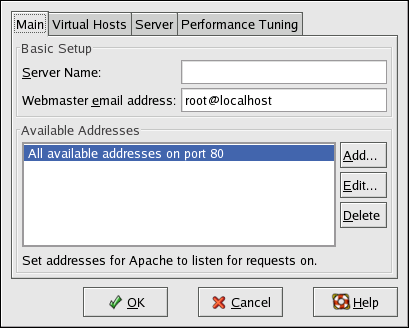
Use the Main tab to configure the basic server settings.
Enter a fully qualified domain name that you have the right to use in the
Server Name text area. This option corresponds to the
ServerName directive in
httpd.conf. The
ServerName directive sets the hostname of the Web server. It is used when creating redirection URLs. If you do not define a server name, the Web server attempts to resolve it from the IP address of the system. The server name does not have to be the domain name resolved from the IP address of the server. For example, you might set the server name to www.example.com while the server's real DNS name is foo.example.com.
Enter the email address of the person who maintains the Web server in the
Webmaster email address text area. This option corresponds to the
ServerAdmin directive in
httpd.conf. If you configure the server's error pages to contain an email address, this email address is used so that users can report a problem to the server's administrator. The default value is root@localhost.
Use the
Available Addresses area to define the ports on which the server accepts incoming requests. This option corresponds to the
Listen directive in
httpd.conf. By default, Red Hat configures the Apache HTTP Server to listen to port 80 for non-secure Web communications.
Click the
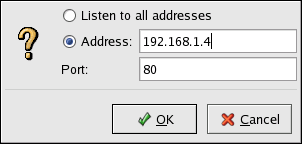
Add button to define additional ports on which to accept requests. A window as shown in
Figure 11.2, “Available Addresses” appears. Either choose the
Listen to all addresses option to listen to all IP addresses on the defined port or specify a particular IP address over which the server accepts connections in the
Address field. Only specify one IP address per port number. To specify more than one IP address with the same port number, create an entry for each IP address. If at all possible, use an IP address instead of a domain name to prevent a DNS lookup failure. Refer to
http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/dns-caveats.html for more information about
Issues Regarding DNS and Apache.
Entering an asterisk (*) in the Address field is the same as choosing Listen to all addresses. Clicking the Edit button in the Available Addresses frame shows the same window as the Add button except with the fields populated for the selected entry. To delete an entry, select it and click the Delete button.
Tip
If you set the server to listen to a port under 1024, you must be root to start it. For port 1024 and above, httpd can be started as a regular user.